What is Visual Basic Editor in Excel?
 What is Visual Basic Editor in Excel?
What is Visual Basic Editor in Excel?

Visual Basic Editor is a separate application that is a part of Excel and opens whenever you open an Excel workbook. By default, it’s hidden and to access it, you need to activate it.
VB Editor is the place where you keep the VB code.
There are multiple ways you get the code in the VB Editor:
- When you record a macro, it automatically creates a new module in the VB Editor and inserts the code in that module.
- You can manually type VB code in the VB editor.
- You can copy a code from some other workbook or from the internet and paste it in the VB Editor.
Opening the VB Editor
There are various ways to open the Visual Basic Editor in Excel:
- Using a Keyboard Shortcut (easiest and fastest)
- Using the Developer Tab.
- Using the Worksheet Tabs.
Let’s go through each of these quickly.
Keyboard Shortcut to Open the Visual Basic Editor
The easiest way to open the Visual Basic editor is to use the keyboard shortcut – ALT + F11 (hold the ALT key and press the F11 key).

As soon as you do this, it will open a separate window for the Visual Basic editor.
This shortcut works as a toggle, so when you use it again, it will take you back to the Excel application (without closing the VB Editor).
The shortcut for the Mac version is Opt + F11 or Fn + Opt + F11
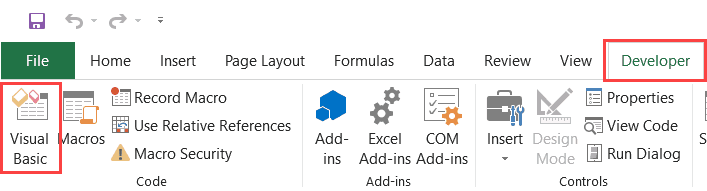
Using the Developer Tab
To open the Visual Basic Editor from the ribbon:
- Click the Developer tab (if you don’t see a developer tab, read this on how to get it).
- In the Code group, click on Visual Basic.
Using the Worksheet Tab
This is a less used method to open the Vb Editor.
Go to any of the worksheet tabs, right-click, and select ‘View Code’.
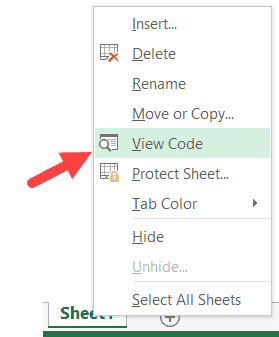
This method wouldn’t just open the VB Editor, it will also take you to the code window for that worksheet object.
This is useful when you want to write code that works only for a specific worksheet. This is usually the case with worksheet events.
Anatomy of the Visual Basic Editor in Excel
When you open the VB Editor for the first time, it may look a bit overwhelming.
There are different options and sections that may seem completely new at first.
Also, it still has an old Excel 97 days look. While Excel has improved tremendously in design and usability over the years, the VB Editor has not seen any change in the way it looks.
In this section, I will take you through the different parts of the Visual Basic Editor application.
Note: When I started using VBA years ago, I was quite overwhelmed with all these new options and windows. But as you get used to working with VBA, you would get comfortable with most of these. And most of the time, you’ll not be required to use all the options, only a hand full.
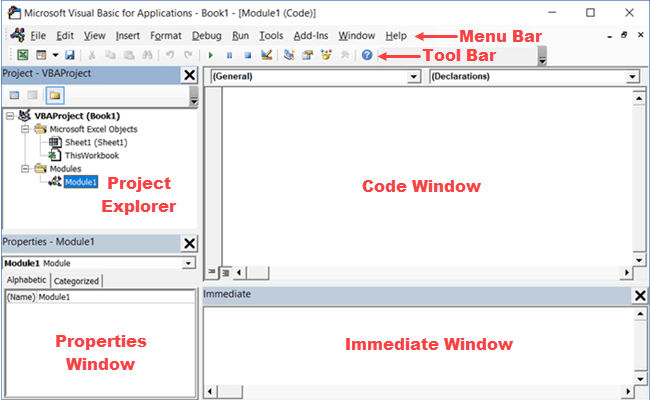
Below is an image of the different components of the VB Editor. These are then described in detail in the below sections of this tutorial.

Now let’s quickly go through each of these components and understand what it does:
Menu Bar
This is where you have all the options that you can use in the VB Editor. It is similar to the Excel ribbon where you have tabs and options with each tab.
You can explore the available options by clicking on each of the menu element.
You will notice that most of the options in VB Editor have keyboard shortcuts mentioned next to it. Once you get used to a few keyboard shortcuts, working with the VB Editor becomes really easy.
Tool Bar
By default, there is a toolbar in the VB Editor which has some useful options that you’re likely to need most often. This is just like the Quick Access Toolbar in Excel. It gives you quick access to some of the useful options.
You can customize it a little by removing or adding options to it (by clicking on the small downward pointing arrow at the end of the toolbar).
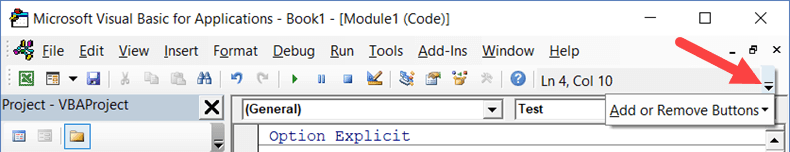
In most cases, the default toolbar is all you need when working with the VB Editor.
You can move the toolbar above the menu bar by clicking on the three gray dots (at the beginning of the toolbar) and dragging it above the menu bar.
Note: There are four toolbars in the VB Editor – Standard, Debug, Edit, and User form. What you see in the image above (which is also the default) is the standard toolbar. You can access other toolbars by going to the View option and hovering the cursor on the Toolbars option. You can add one or more toolbars to the VB Editor if you want.
Project Explorer
Project Explorer is a window on the left that shows all the objects currently open in Excel.
When you’re working with Excel, every workbook or add-in that is open is a project. And each of these projects can have a collection of objects in it.
For example, in the below image, the Project Explorer shows the two workbooks that are open (Book1 and Book2) and the objects in each workbook (worksheets, ThisWorkbook, and Module in Book1).
There is a plus icon to the left of objects that you can use to collapse the list of objects or expand and see the complete list of objects.
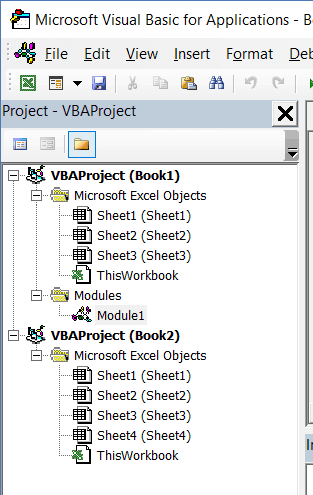
The following objects can be a part of the Project Explorer:
- All open Workbooks – within each workbook (which is also called a project), you can have the following objects:
- Worksheet object for each worksheet in the workbook
- ThisWorkbook object which represents the workbook itself
- Chartsheet object for each chart sheet (these are not as common as worksheets)
- Modules – This is where the code that is generated with a macro recorder goes. You can also write or copy-paste VBA code here.
- All open Add-ins
Consider the Project Explorer as a place that outlines all the objects open in Excel at the given time.
The keyboard shortcut to open the Project Explorer is Control + R (hold the control key and then press R). To close it, simply click the close icon at the top right of the Project Explorer window.
Note: For every object in Project Explorer, there is a code window in which you can write the code (or copy and paste it from somewhere). The code window appears when you double click on the object.
Properties Window
Properties window is where you get to see the properties of the select object. If you don’t have the Properties window already, you can get it by using the keyboard shortcut F4 (or go to the View tab and click Properties window).
Properties window is a floating window which you can dock in the VB Editor. In the below example, I have docked it just below the Project Explorer.
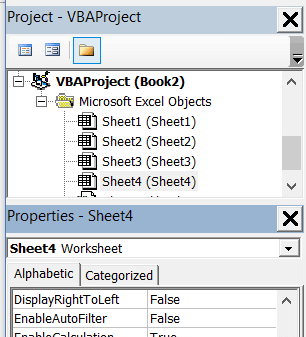
Properties window allows us to change the properties of a selected object. For example, if I want to make a worksheet hidden (or very hidden), I can do that by changing the Visible Property of the selected worksheet object.
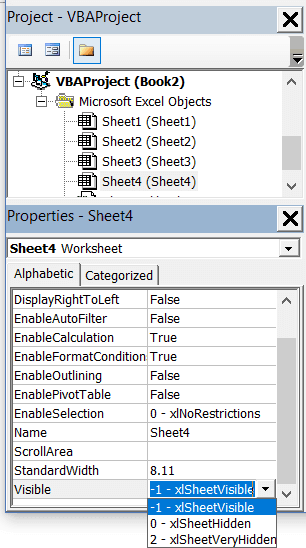
Related: Hiding a Worksheet in Excel (that can not be un-hidden easily)
Code Window
There is a code window for each object that is listed in the Project Explorer. You can open the code window for an object by double-clicking on it in the Project Explorer area.
Code window is where you’ll write your code or copy paste a code from somewhere else.
When you record a macro, the code for it goes into the code window of a module. Excel automatically inserts a module to place the code in it when recording a macro.
Related: How to Run a Macro (VBA Code) in Excel.
Immediate Window
The Immediate window is mostly used when debugging code. One way I use the Immediate window is by using a Print.Debug statement within the code and then run the code.
It helps me to debug the code and determine where my code gets stuck. If I get the result of Print.Debug in the immediate window, I know the code worked at least till that line.
If you’re new to VBA coding, it may take you some time to be able to use the immediate window for debugging.
By default, the immediate window is not visible in the VB Editor. You can get it by using the keyboard shortcut Control + G (or can go to the View tab and click on ‘Immediate Window’).
Where to Add Code in the VB Editor
I hope you now have a basic understanding of what VB Editor is and what all parts it has.
In this section of this tutorial, I will show you where to add a VBA code in the Visual Basic Editor.
There are two places where you can add the VBA code in Excel:
- The code window for an object. These objects can be a workbook, worksheet, User Form, etc.
- The code window of a module.
Module Code Window Vs Object Code Window
Let me first quickly clear the difference between adding a code in a module vs adding a code in an object code window.
When you add a code to any of the objects, it’s dependent on some action of that object that will trigger that code. For example, if you want to unhide all the worksheets in a workbook as soon as you open that workbook, then the code would go in the ThisWorkbook object (which represents the workbook).
The trigger, in this case, is opening the workbook.
Similarly, if you want to protect a worksheet as soon as some other worksheet is activated, the code for that would go in the worksheet code window.
These triggers are called events and you can associate a code to be executed when an event occurs.
Related: Learn more about Events in VBA.
On the contrary, the code in the module needs to be executed either manually (or it can be called from other subroutines as well).
When you record a macro, Excel automatically creates a module and inserts the recorded macro code in it. Now if you have to run this code, you need to manually execute the macro.
Adding VBA Code in Module
While recording a macro automatically creates a module and inserts the code in it, there are some limitations when using a macro recorder. For example, it can not use loops or If Then Else conditions.
In such cases, it’s better to either copy and paste the code manually or write the code yourself.
A module can be used to hold the following types of VBA codes:
- Declarations: You can declare variables in a module. Declaring variables allows you to specify what type of data a variable can hold. You can declare a variable for a sub-routine only or for all sub-routines in the module (or all modules)
- Subroutines (Procedures): This is the code that has the steps you want VBA to perform.
- Function Procedures: This is a code that returns a single value and you can use it to create custom functions (also called User Defined Functions or UDFs in VBA)
By default, a module is not a part of the workbook. You need to insert it first before using it.
Adding a Module in the VB Editor
Below are the steps to add a module:
- Right-click on any object of the workbook (in which you want the module).

- Hover the cursor on the Insert option.
- Click on Module.

This would instantly create a folder called Module and insert an object called Module 1. If you already have a module inserted, the above steps would insert another module.
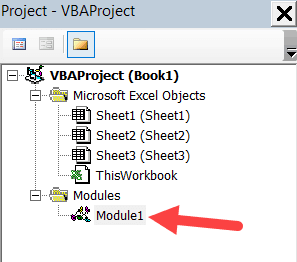
Once the module is inserted, you can double click on the module object in the Project Explorer and it will open the code window for it. Now you can copy paste the code or write it yourself.
Removing the Module
Below are the steps to remove a module in Excel VBA:
- Right-click on the module that you want to remove.
- Click on Remove Module option.

- In the dialog box that opens, click on No.

Note: You can export a module before removing it. It gets saved as a .bas file and you can import it in some other project. To export a module, right-click on the module and click on ‘Export file’.
Adding Code to the Object Code Window
To open the code window for an object, simply double-click on it.
When it opens, you can enter the code manually or copy paste the code from other modules or from the internet.
Note that some of the objects allow you to choose the event for which you want to write the code.
For example, if you want to write a code for something to happen when selection is changed in the worksheet, you need to first select worksheet from the drop down at the top left of the code window and then select the change event from the drop-down on the right.
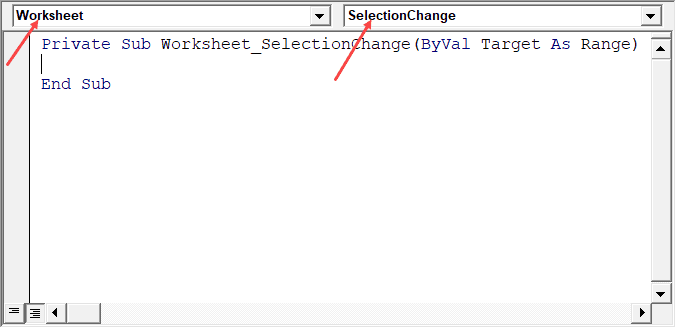
Note: These events are specific to the object. When you open the code window for a workbook, you will see the events related to the workbook object. When you open the code window for a worksheet, you will see the events related to the worksheet object.
Customizing the VB Editor
While the default settings of the Visual Basic Editor are good enough for most users, it does allow you to further customize the interface and a few functionalities.
In this section of the tutorial, I will show you all the options you have when customizing the VB Editor.
To customize the VB Editor environment, click Tools in the menu bar and then click on Options.
This would open the Options dialog box which will give you all the customization options in the VB Editor. The ‘Options’ dialog box has four tabs (as shown below) that have various customizations options for the Visual Basic Editor.
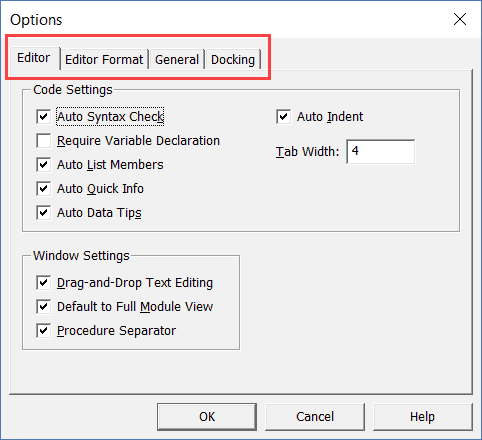
Let’s quickly go through each of these tabs and the important options in each.
Editor Tab
While the inbuilt settings work fine in most cases, let me still go through the options in this tab.
As you get more proficient working with VBA in Excel, you may want to customize the VB Editor using some of these options.
Auto Syntax Check
When working with VBA in Excel, as soon as you make a syntax error, you will be greeted by a pop-up dialog box (with some description about the error). Something as shown below:
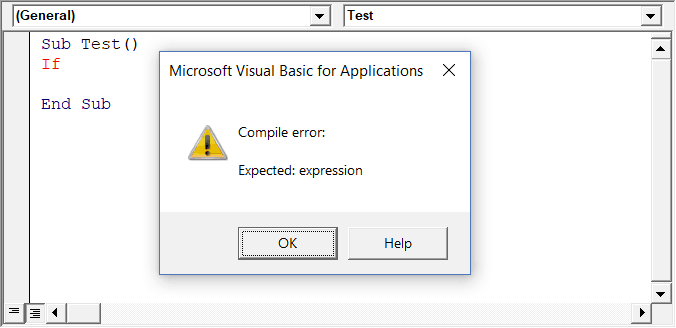
If you disable this option, this pop-up box will not appear even when you make a syntax error. However, there would be a change in color in the code text to indicate that there is an error.
If you’re a beginner, I recommend you keep this option enabled. As you get more experienced with coding, you may start finding these pop-up boxes irritating, and then you can disable this option.
Require Variable Declaration
This is one option I recommend enabling.
When you’re working with VBA, you would be using variables to hold different data types and objects.
When you enable this option, it automatically inserts the ‘Option Explicit’ statement at the top of the code window. This forces you to declare all the variables that you’re using in your code. If you don’t declare a variable and try to execute the code, it will show an error (as shown below).
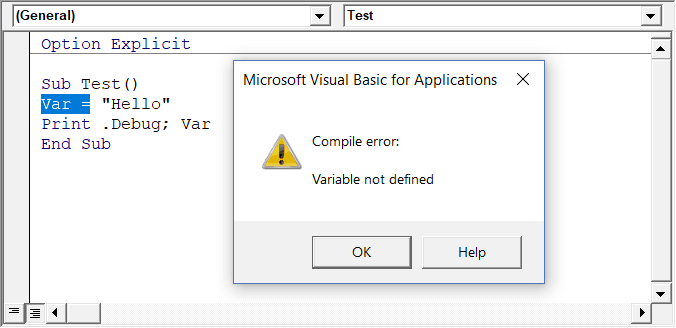
In the above case, I used the variable Var, but I didn’t declare it. So when I try to run the code, it shows an error.
This option is quite useful when you have a lot of variables. It often helps me find misspelled variables names as they are considered as undeclared and an error is shown.
Note: When you enable this option, it does not impact the existing modules.
Auto List Member
This option is quite useful as it helps you get a list of properties of methods for an object.
For example, if I want to delete a worksheet (Sheet1), I need to use the line Sheet1.Delete.
While I am typing the code, as soon as I type the dot, it will show me all the methods and properties associated with the Worksheet object (as shown below).
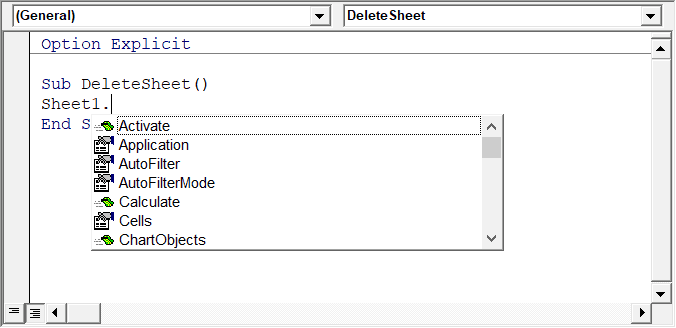
Auto list feature is great as it allows you to:
- Quickly select the property and method from the list and saves time
- Shows you all the properties and methods which you may not be aware of
- Avoid making spelling errors
This option is enabled by default and I recommend keeping it that way.
Auto Quick Info Options
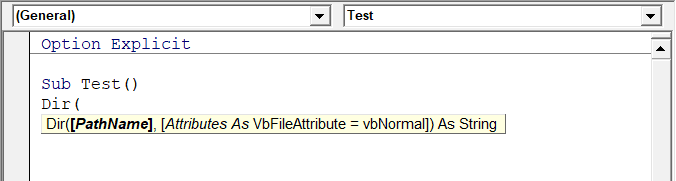
When you type a function in Excel worksheet, it shows you some information about the function – such as the arguments it takes.
Similarly, when you type a function in VBA, it shows you some information (as shown below). But for that to happen, you need to make sure the Auto Quick Info option is enabled (which it is by default).
Auto Data Tips Options
When you’re going through your code line by line and place your cursor above a variable name, it will show you the value of the variable.
I find it quite useful when debugging the code or going through the code line by line which has loops in it.
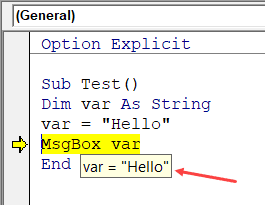
In the above example, as soon as I put the cursor over the variable (var), it shows the value it holds.
This option is enabled by default and I recommend you keep it that way.
Auto Indent
Since VBA codes can get long and messy, using indentation increases the readability of the code.
When writing code, you can indent using the tab key.
This option ensures that when you are done with the indented line and hit enter, the next line doesn’t start from the very beginning, but has the same indentation as the previous line.
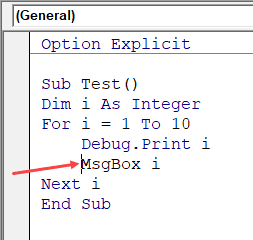
In the above example, after I write the Debug.Print line and hit enter, it will start right below it (with the same indentation level).
I find this option useful and turning this off would mean manually indenting each line in a block of code that I want indented.
You can change the indentation value if you want. I keep it at the default value.
Drag and Drop Text Editing
When this option is enabled, it allows you to select a block of code and drag and drop it.
It saves time as you don’t have to first cut and then pastes it. You can simply select and drag it.
This option is enabled by default and I recommend you keep it that way.
Default to Full Module View
When this option is enabled, you will be able to see all the procedures in a module in one single scrollable list.
If you disable this option, you will only be able to see one module at a time. You will have to make a selection of the module you want to see from the drop down at the top right of the code window.
This option is enabled by default and I recommend keeping it that way.
One reason you may want to disable it when you have multiple procedures that are huge and scrolling across these is taking time, or when you have a lot of procedures and you want to quickly find it instead of wasting time in scrolling.
Procedure Separator
When this option is enabled, you will see a line (a kind of divider) between two procedures.
I find this useful as it visually shows when one procedure ends and the other one starts.
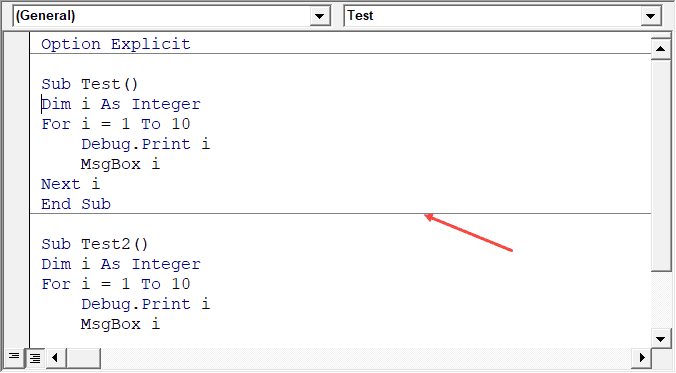
It’s enabled by default and I recommend keeping it that way.
Editor Format Tab
With the options in the Editor Format tab, you can customize the way your code looks in the code window.
Personally, I keep all the default options as I am fine with it. If you want, you can tweak this based on your preference.
To make a change, you need to first select an option in the Code Colors box. Once an option is selected, you can modify foreground, background, and the indicator color for it.
The font type and font size can also be set in this tab. It’s recommended to use a fixed-width font such as Courier New, as it makes the code more readable.
Note that the font type and size setting will remain the same for all code types (i.e., all the code types shown in the code color box).
Below is an image where I have selected Breakpoint, and I can change the formatting of it.
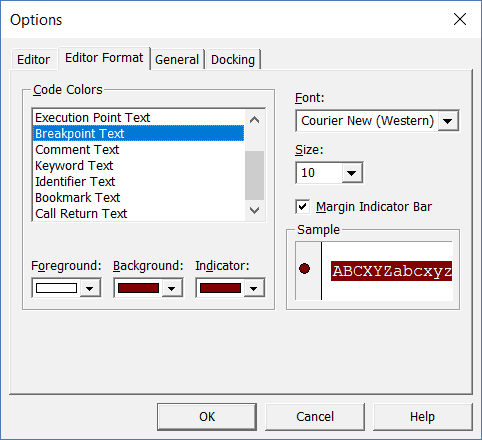
Note: The Margin Indicator Bar option when enabled shows a little margin bar to the left of the code. It’s helpful as it shows useful indicators when executing the code. In the above example, when you set a breakpoint, it will automatically show a red dot to the left of the line in the margin bar. Alternatively, to set a breakpoint, you can simply click on the margin bar on the left of the code line that you want as the breakpoint.
By default, Margin Indicator Bar is enabled and I recommend keeping it that way.
One of my VBA course students found this customization options useful and she was color blind. Using the options here, she was able to set the color and formats that made it easy for her to work with VBA.
General Tab
General tab has many options but you don’t need to change any of it.
I recommend you keep all the options as is.
One important option to know about in this tab is Error Handling.
By default, ‘Break on Unhandled Errors’ is selected and I recommend keeping it that way.
This option means that if your code encounters an error, and you have not handled that error in your code already, then it will break and stop. But if you have addressed the error (such as by using On Error Resume Next or On Error Goto options), then it will not break (as the errors are not unhandled).
Docking Tab
In this tab, you can specify which windows you want to get docked.
Docking means that you can fix the position of a window (such as project explorer or the Properties window) so that it doesn’t float around and you can view all the different windows at the same time.
If you don’t dock, you will be able to view one window at a time in full-screen mode and will have to switch to the other one.
I recommend keeping the default settings.
#evba #etipfree #kingexcel📤You download App EVBA.info installed directly on the latest phone here : https://www.evba.info/p/app-evbainfo-setting-for-your-phone.html?m=1































Leave a Comment